Forgings
Why Choose Forging?
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of a metal through hammering, pressing, or rolling. These compressive forces are delivered with a hammer or die. Forging is often categorised according to the temperature at which it is performed — cold, warm, or hot forging.
WELD2CAST’s considerable experience enables us to produce engineered forgings in an extensive range of materials including carbon, alloy, stainless and heat-resisting steels. In addition, we also produce in non-ferrous materials, aluminium, copper, and brass.
Typical heat treatment techniques applied to our forgings include hardening, tempering, annealing, normalising, stress relieving, and solution annealing

WELD2CAST Can Offer Different Forging Techniques
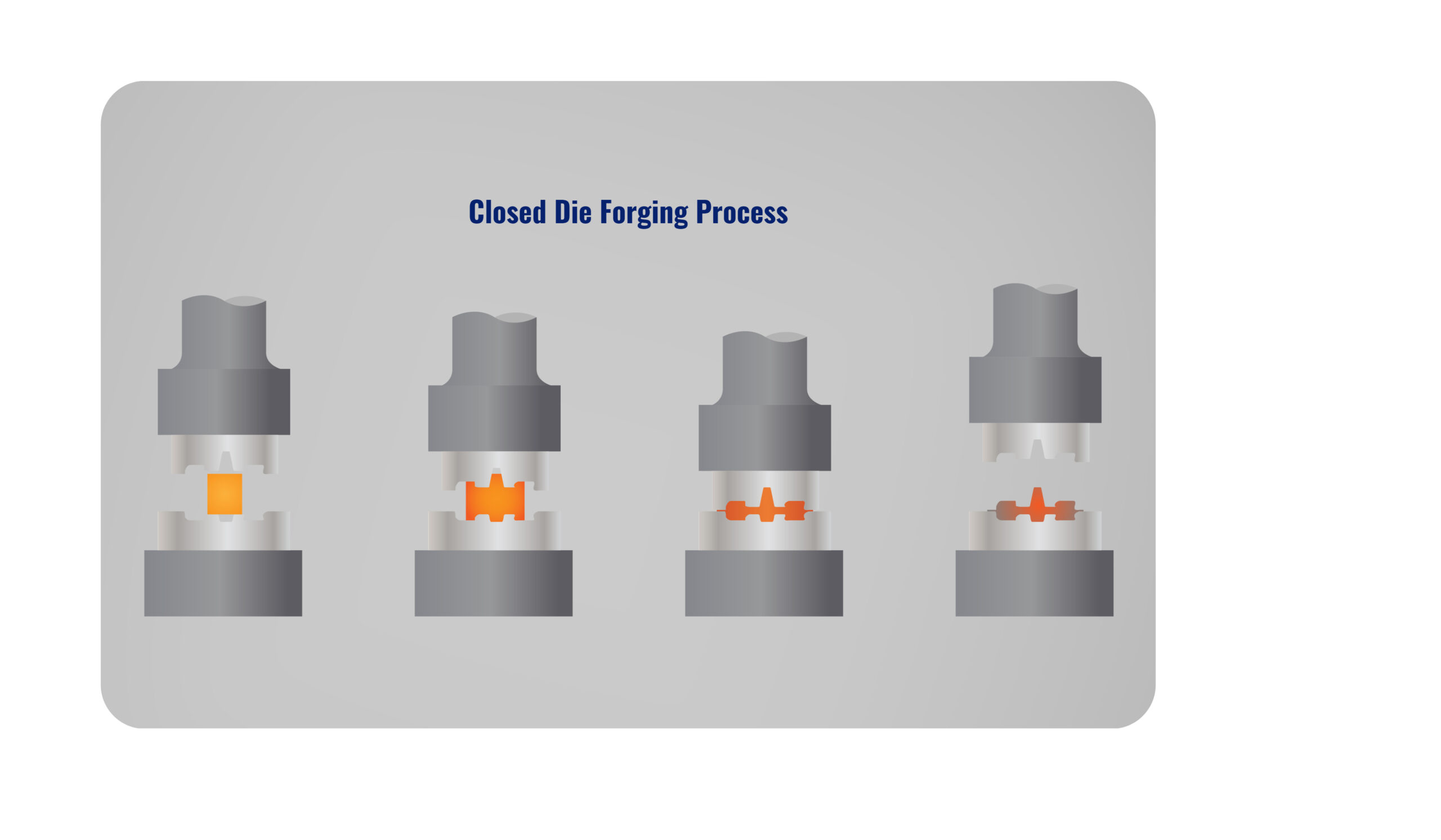
- Closed Die Forgings (Precision forgings)
- Open Die Forgings
- Cold Forgings
- Seamless and Rolled Ring forgings

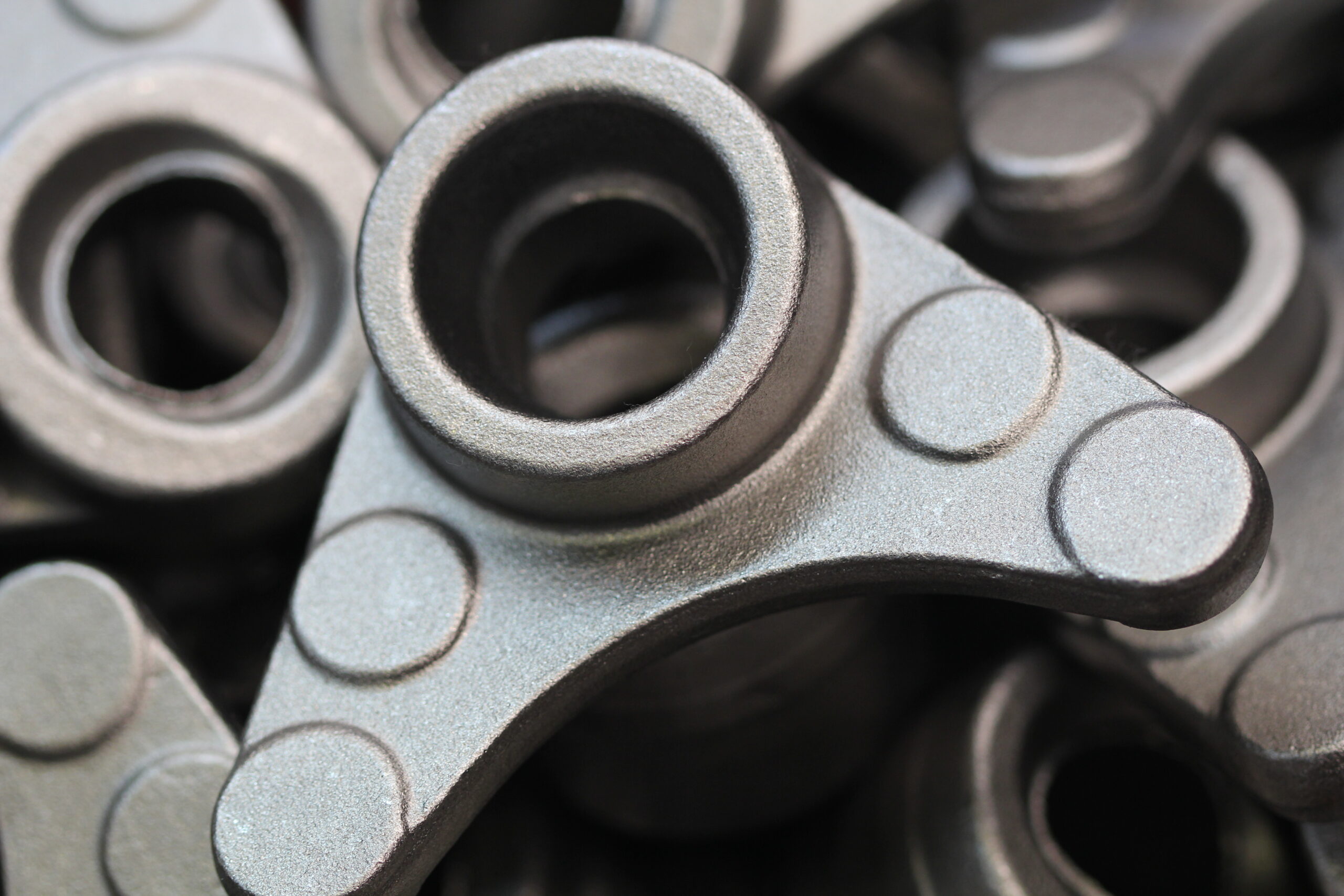
WELD2CAST’s Strengths and Benefits Of Engineered Forgings
- No minimum order quantity.
- Forged precision components from 25 gram up to 75 kg/pcs net weight.
- Small & medium batch sizes are a specialty.
- Converting and design of machined-from-solid components or weldments into engineered forgings .
- Technically challenging forged components are a specialty.
- Experts in low+high alloy steel and aluminium forgings.
- Manufactured to international forging standards and specifications: EN10243-1 and EN10243-2.

Closed Die Forgings vs Investment Casting
In contrast to Closed Die Forging (precision forging), Investment Casting (precision casting) is the casting method of pouring liquid metal into moulds to form the shapes. The same principles are used in these two methods, however, both Investment Casting and Closed Die Forging can manufacture components in accurate dimensions and tolerances. What is important to note is that defects may occur in investment casting, which could be effectively avoided in closed die forging.